Речиц Виталий
Ukrainian realities in protection of intellectual property law in the Internet
Ukrainian realities in protection of intellectual property law in the Internet
The modern rates of Internet development and turnover of information between users create the new industries and niches for business development, creativity and entertainment nowadays.
Anyone who has unique and inimitable information, from a simple user to mega corporations, move them to the Internet, in such a way receiving their own digital copies, generating interactive products and applications with the common purpose to stand out and attract attention.
Ukraine is a country that during 24 years of independence goes through the way of cardinal reformation from the industrial Socialist Republic to the Informational capitalist state.
Availability of modern intellectual property system is an essential element to stimulate the development of high-precision technologies and the economy in general.
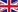
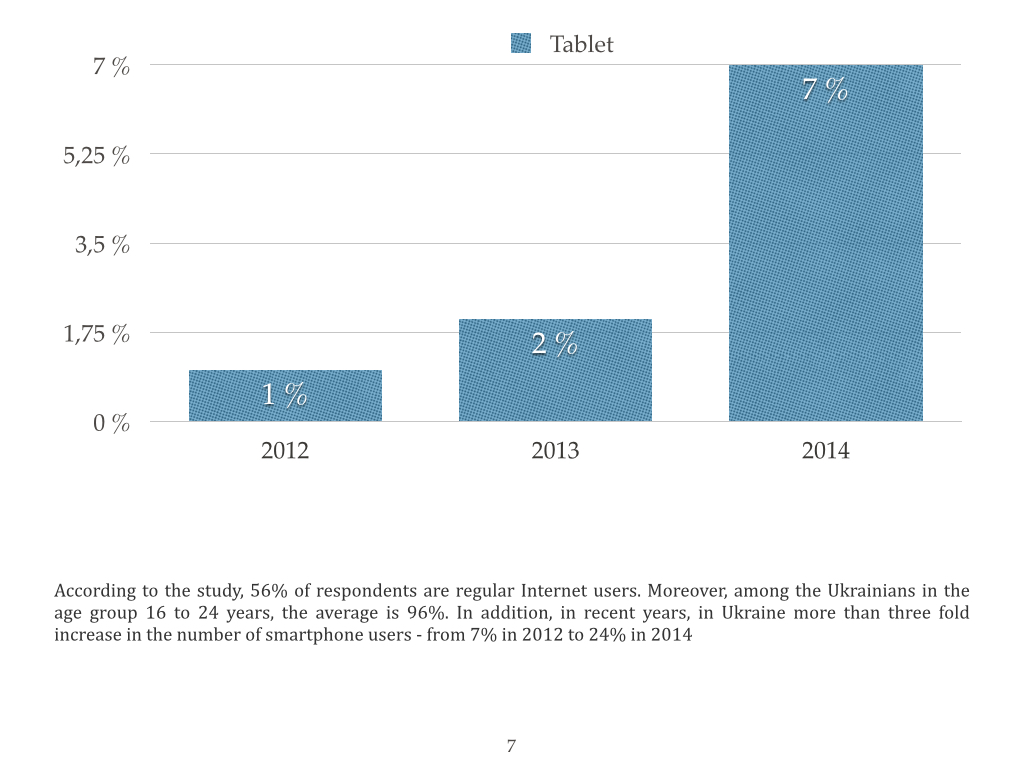
I offer you a portrait of Ukrainian Internet user that was compiled by TNS Infatest by the request of Google.
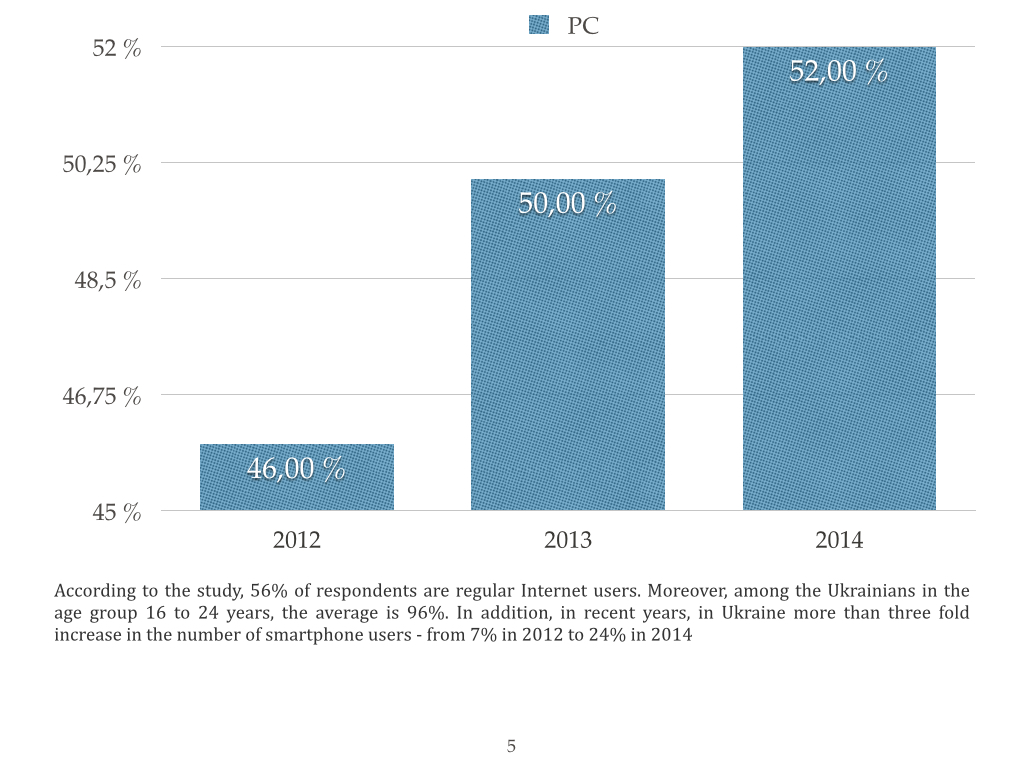
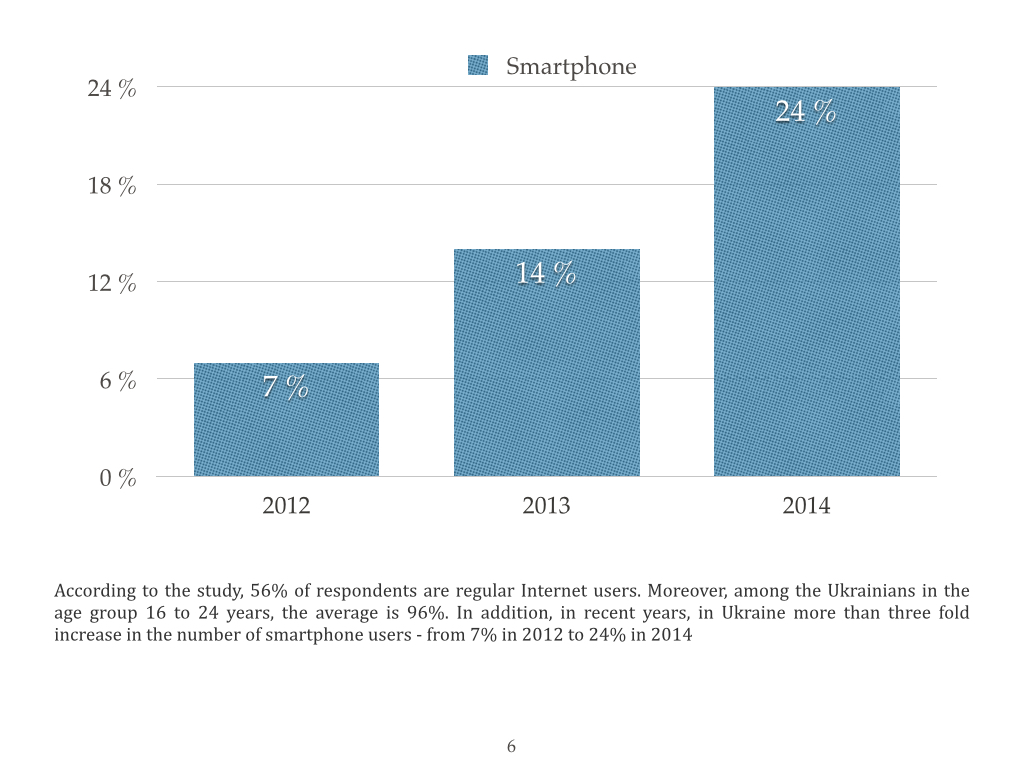
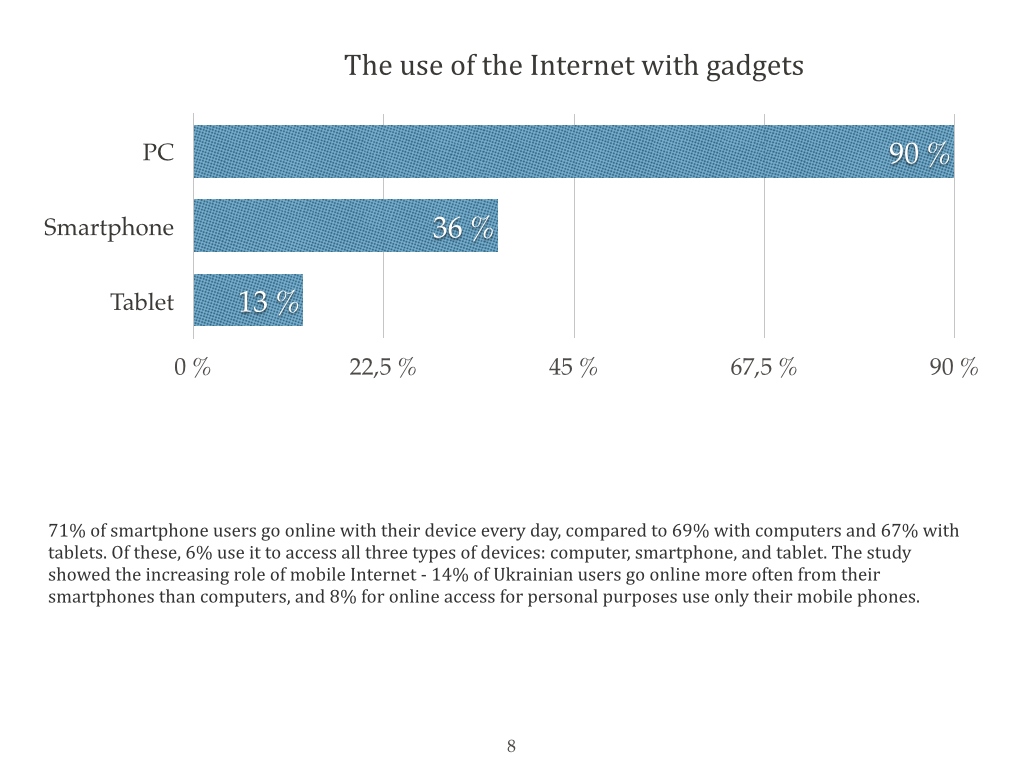
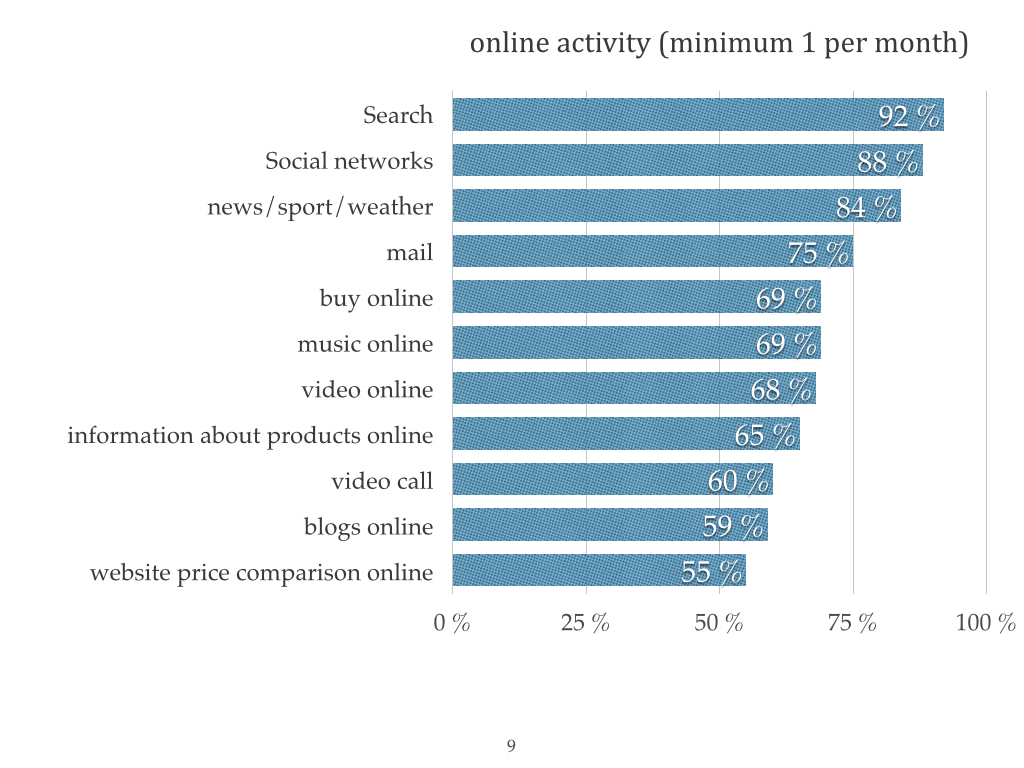
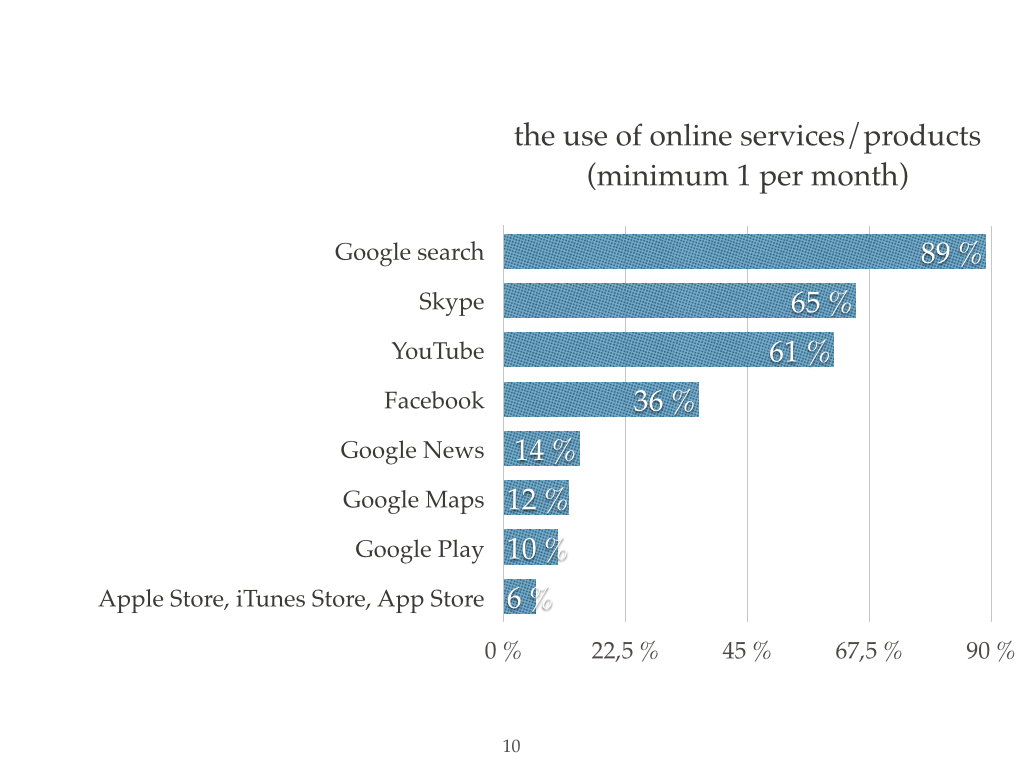

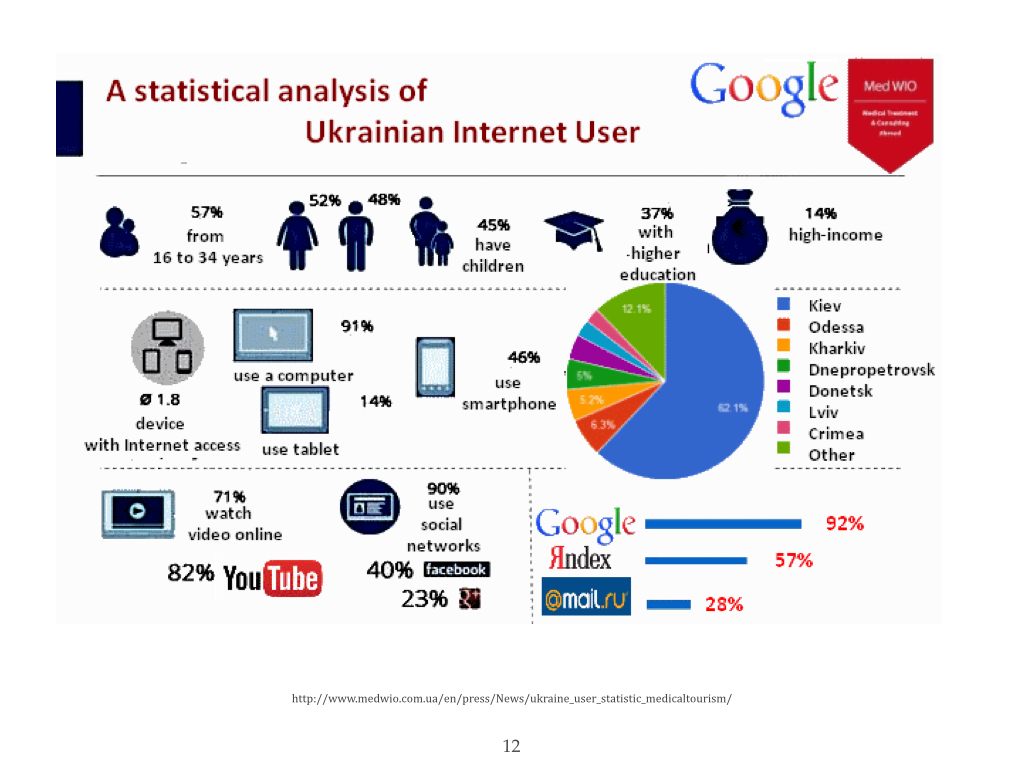
There is the problem today that is related to the legal protection of intellectual property in Ukraine, particularly with the copyright infringements on the Internet.
It is shown in the following ways:
1. piracy;
2. rip-off;
3. fake;
4. the changing of information.
The reasons that promote it:
- The absence of legal copyright protection in the Internet;
- The rapid development of new social relations that are not regulated by the law;
- The low purchasing power of the population of the country.
The most common ways of copyright violations in the Internet are:
- Copying of the materials for further dissemination,
- The text transformation to the electronic version in order to posting in the Internet.
National law of Ukraine in the field of protection of copyright and related rights.
The Constitution of Ukraine:
Article 54
Citizens are guaranteed the freedom of literary, artistic, scientific and technical creativity, protection of intellectual property, their copyrights, moral and material interests that arise with regard to various types of intellectual activity.
Every citizen has the right to the results of his or her intellectual, creative activity; no one shall use or distribute them without his or her consent, with the exceptions established by law.
The State promotes the development of science and the establishment of scientific relations of Ukraine with the world community.
CIVIL CODE OF UKRAINE
BOOK FOUR – INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT
Chapter 35. GENERAL PROVISIONS ABOUT INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT
Article 418. The Notion of Intellectual Property Right
1. Intellectual property right shall be the rights of an entity to the results of intellectual, creative
activity or to another object of intellectual property right established by this Code and by the
other law.
2. Intellectual property right shall consist of personal non-proprietary intellectual rights and/or
proprietary intellectual rights, the contents thereof with respect to specific objects of
intellectual property rights are established by this Code and by the other law.
3. Intellectual property right shall be inviolable: no person can be deprived of the intellectual
property right or restricted in the exercise thereof, except for the cases stipulated by the law.
CRIMINAL CODE OF UKRAINE
Article 176. Violation of copyright and allied rights
1. Illegal reproduction or distribution of scientific, literary, or art works, computer software or databases, and also illegal reproduction, distribution of performances, phonograms and broadcast programs, making their illegal copies and distribution on audio and video tapes, disks, and other media, or other violation of copyright and allied rights, where such actions caused a significant pecuniary loss, -
shall be punishable by a fine of 200 to 1000 tax-free minimum incomes, or correctional labor for a term up to two years, or imprisonment for the same term, with the forfeiture and destruction of all copies of works, material media with computer software, databases, performances, phonograms, broadcast programs, and the equipment and material designated for their production and reproduction.
2. The same actions, if repeated or upon their prior conspiracy of a group of persons, or where they caused a gross pecuniary loss, -
shall be punishable by a fine of 1000 to 2000 tax-free minimum incomes, or correctional labor for a term up to two years, or imprisonment for a term of two to five years, with the forfeiture and destruction of all copies of works, material media with computer software, databases, performances, phonograms, broadcast programs, and the equipment and material designated for their production and reproduction.
3. Any such actions as provided for by paragraph 1 or 2 of this Article, where committed by an official through abuse of office or by organized group of persons, or where they caused a especially gross pecuniary loss, -
shall be punishable by a fine of 2000 to 3000 tax-free minimum incomes, or imprisonment for a term of three to six years, with or without the deprivation of the right to occupy certain positions or engage in certain activities for a term up to three years, and with the forfeiture and destruction of all copies of works, material media with computer software, databases, performances, phonograms, broadcast programs, and the equipment and material designated for their production and reproduction.
Law of Ukraine "On Copyright and Related Rights".
The Legislation of Ukraine in the field of protection of intellectual property, particularly copyright, does not meet the challenges of our time.
This fact is explained by the rapid development of information technology.
Of course, during the creation of copyright law it was not expected.
Now this issue is relevant, as the number of copyright violations in the Internet is growing.
It should be noted that copyright violation on the Internet is due to:
- users does not know the extents of the free using of objects of copy right, because of the lack of information;
- The users know about copyright, but they violate it with the intent.
The main reason for this – the simplicity in obtaining of electronic copies of various objects and the relatively low costing.
Foreign law
The experience of USA:
In this country in 1998 was adopted Digital Millennium Copyright Act (further - DMCA) – the Law "On Protection of copyrighting in the digital age."
Nowadays, it is the most progressive document adopted in order to sort the legal regulation of the Internet.
This legal act contains an important limitation of liability for copyright violations.
According to Art. All 202 DMCA the copyright objects that present on the Internet, are protected.
But any person released from liability for copyright violations if a person doesn’t know about that.
The Act provides for the offenders notification in any of three ways:
1. by letter;
2. by telegram;
3. or via e-mail.
If during a reasonable time the receiver of warning does not delete the object of copyright, it can be applied penalties for violations. For removing an object from the web copyright they involve the provider.
It is also important to note, that Law "On Protection of copyright in the digital age" provides Protection only to original work in greater extent.
Works posted on the Internet, as a rule, are replicas or part of the original work.
If the pirate copy of the film made before the official premiere, there is the criminal liability for violation of intellectual property rights.
But if the pirate copy of the film made after the official premiere, it provides a penalty in lost benefits.
So we can make a conclusion that the right of the United States provides a compromise copyright protection on the Internet, according to which protection is provided without violating the rights to copy, transfer, share and receive information.
US law is trying to eliminate the violation of helping a person who accidentally violated the law in the case to identify the illegal spread of copyright.
The experience of Great Britain:
The main document in the field of copyright in the UK is “Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1988” that determines common rules in the field of copyright protection.
There is one more document – the Copyright and Related Rights Regulations 2003, which brings copyright Britain to European law.
In the Copyright and Related Rights Regulations 2003 suggests that the transfer of information from one person to another by creating a temporary copy is not a violation of the rights of the author (except for the transmission of copies of objects such as computer programs and databases).
Only if such action is carried out without a commercial purpose.
By this way any liability gets off for the useing of copyright material posted on the Internet.
We can see a cardinal difference with US law. In Great Britain, protection is provided, but with previous warning the intruder.
The Chinese experience
The main legal act in this country in the field of copyright protection is the Law "On Copyright of Republic Of China." In general, according to this Act, copyright protection starts with the creation of the work, and its registration serves only to verify the start time of protection in the case of judicial protection.
It should be noted that during the practical activities in China was developed a system of protection of intellectual property rights, which is characterizes in both administrative and legal protection.
Responsibility for copyright violations on the Internet in China is not only for the offender, but also for a company providing services (ISP).
Administrative protection lies in the fact that the ISP should close access to materials that violate copyrights, or delete them from the web, if he finds them.
As a result, providers are forced to close down the whole network segments, avoiding prosecution for copyright violation.
As a result, we can see the benefits of the rights of foreign Internet users in front of Chinese.
Police statistics criminal violations of intellectual property in Ukraine
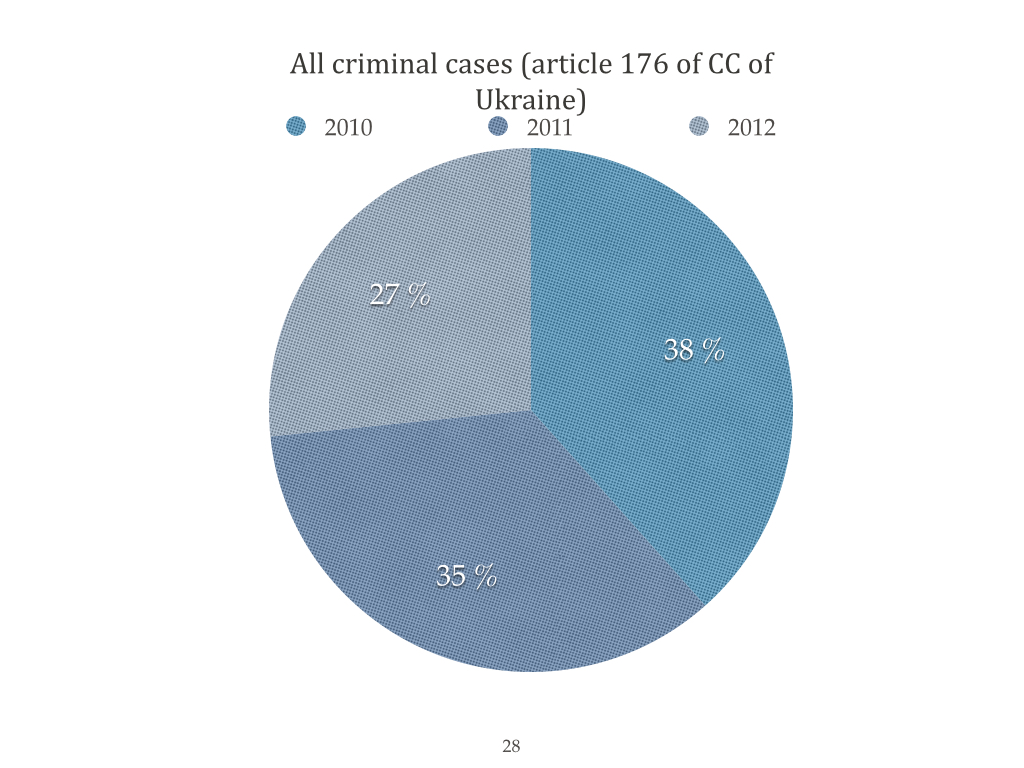
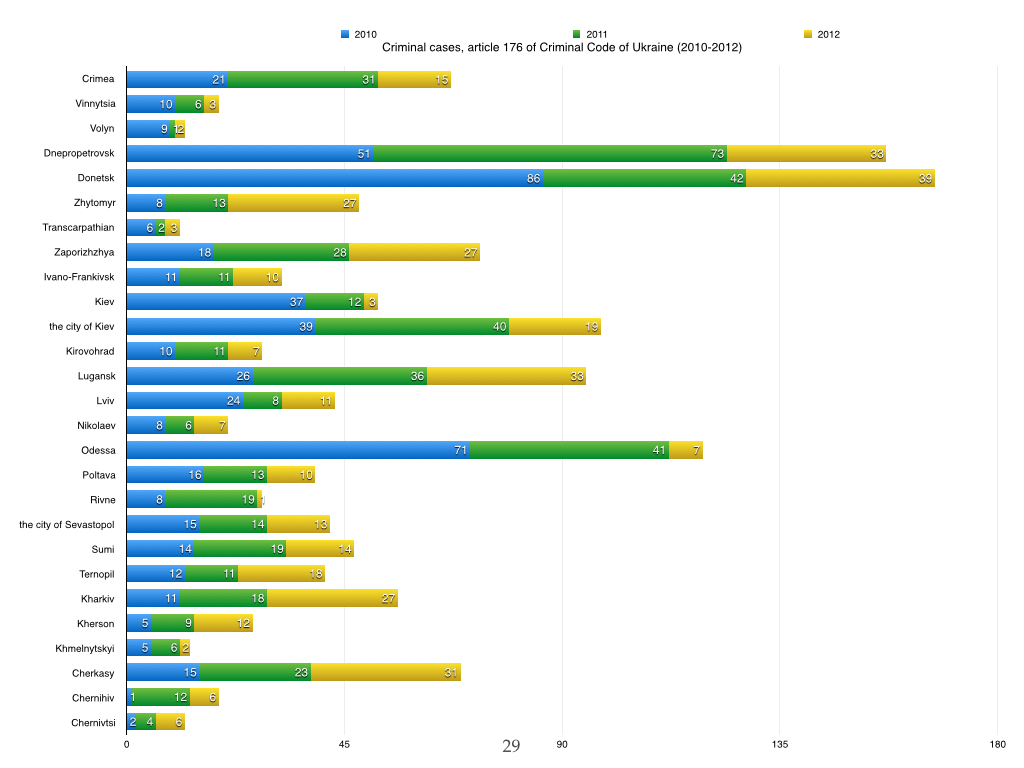
Court statistics sentences in intellectual property in Ukraine
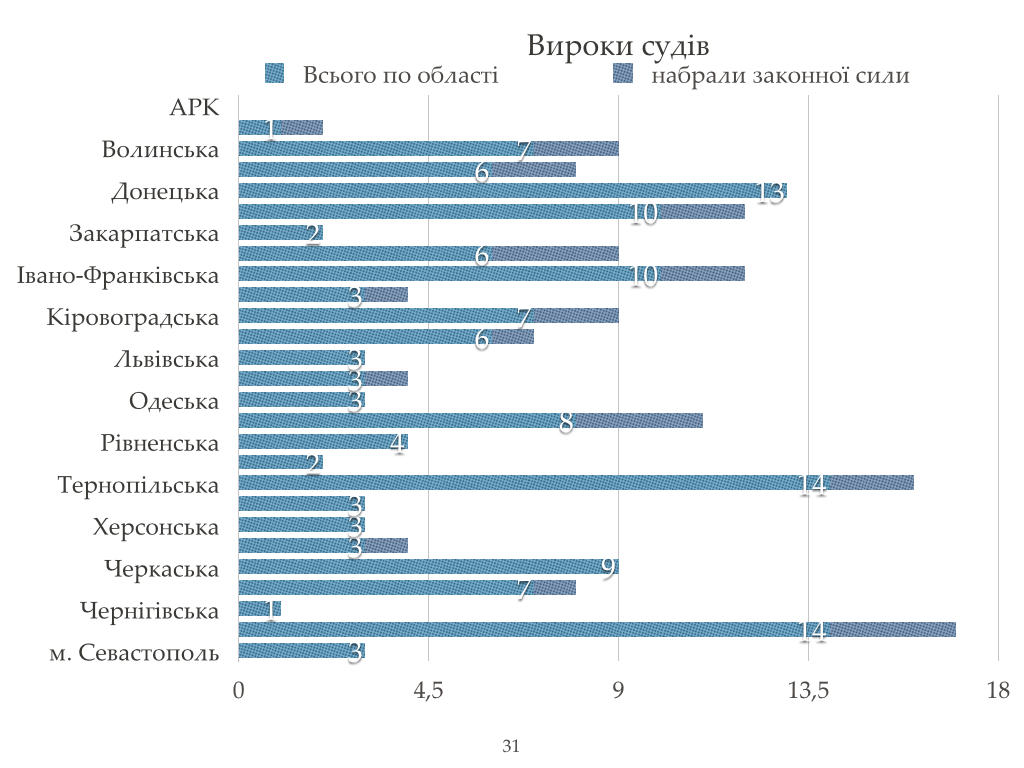
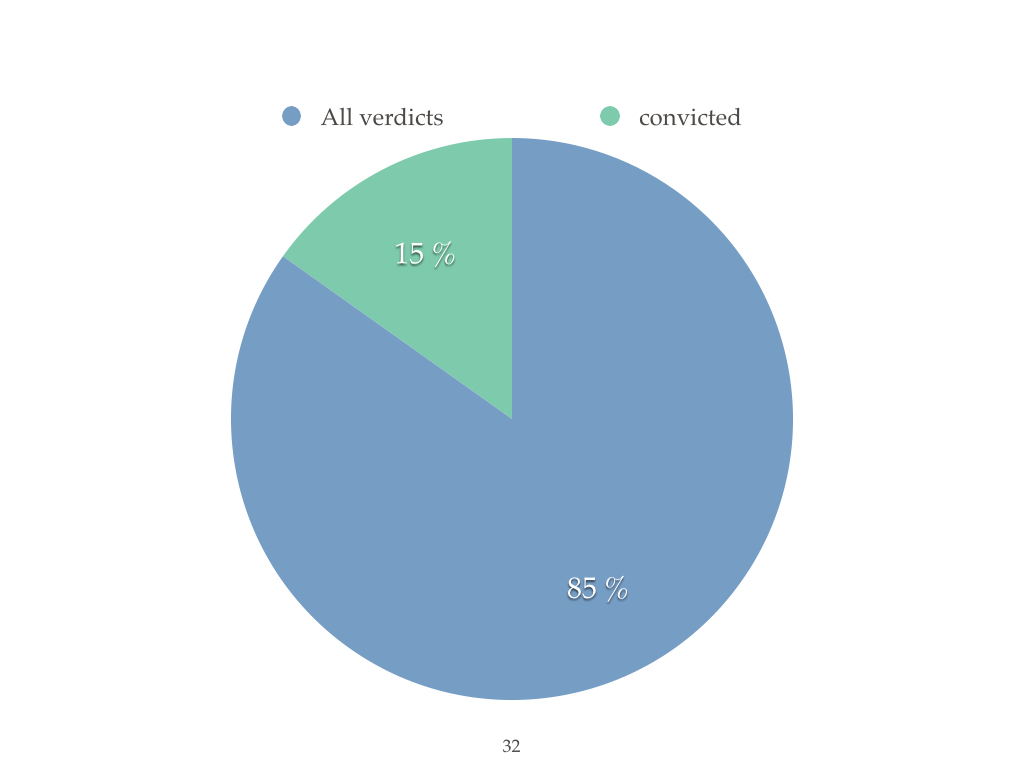
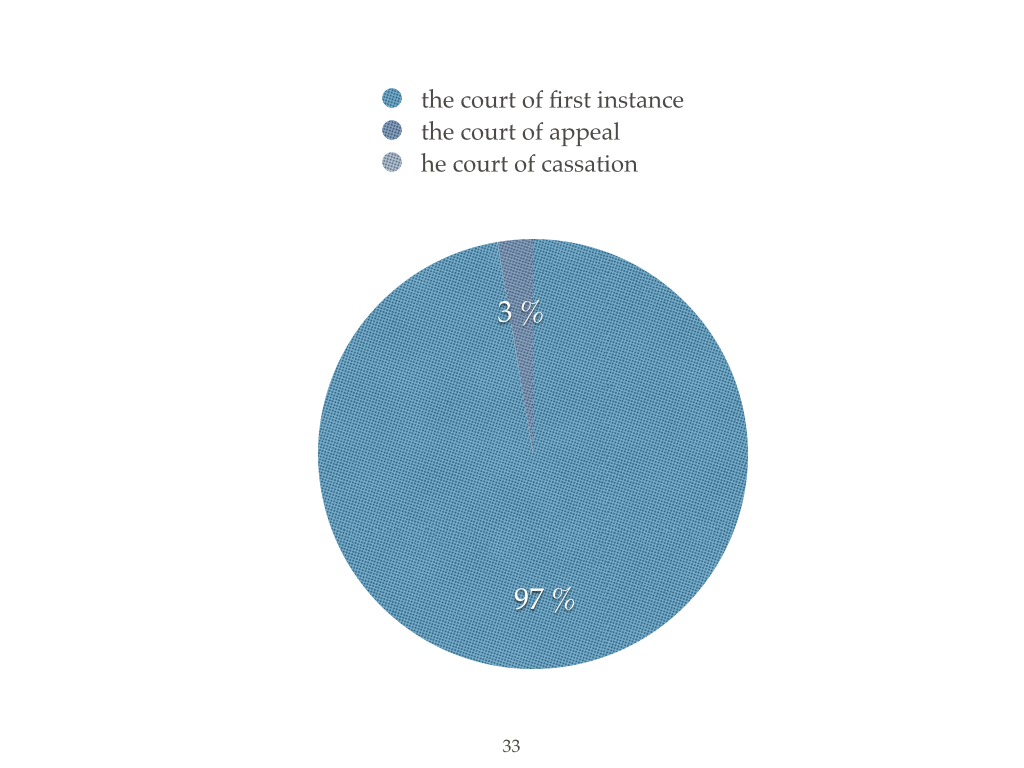
The effectiveness of judicial and police system in Ukraine
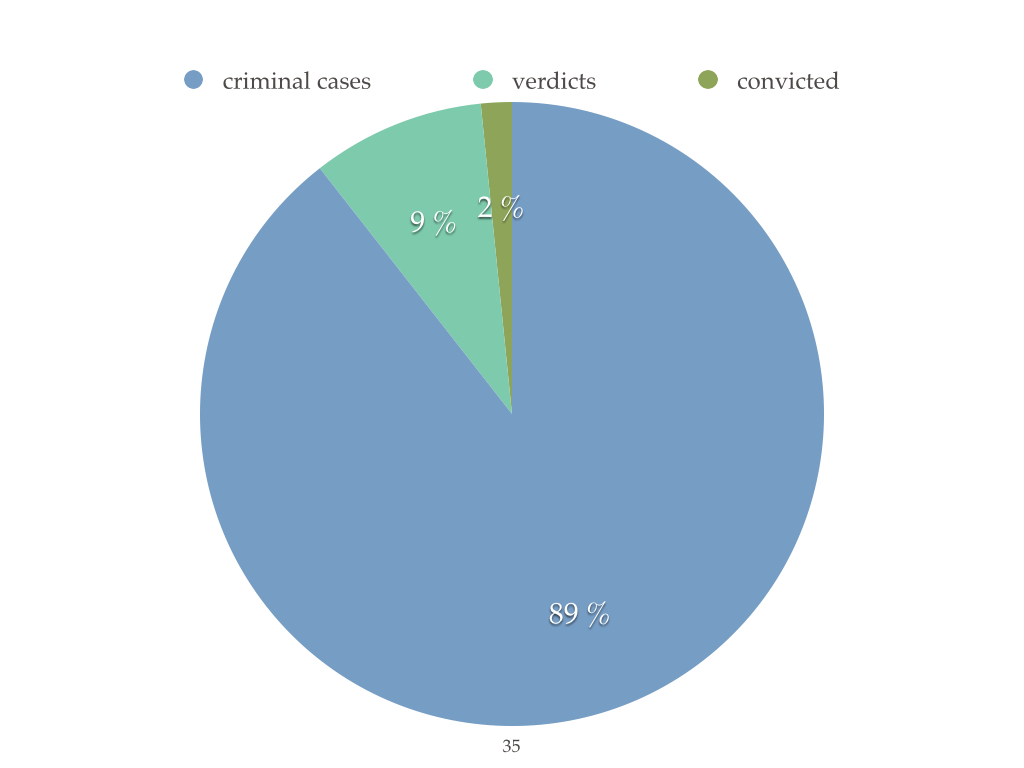
How to protect intellectual property rights on the Internet?